Average Salaries in Japan by Industry (Updated 2025)
Japan’s high cost of living makes it important for job seekers, international professionals, and students to understand what salaries look like here. In 2025, pay levels differ greatly depending on location, industry, and experience. This guide breaks down salary averages across key sectors, compares them to global standards, and offers tips for negotiating a better package in Japan.

Overall Salary Trends in 2025
According to different data sources from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) and major recruitment platforms include indeed, linkedIn, the national average annual salary in Japan is approximately:
- ¥4.5 million (~$31,000 USD) for all workers
- ¥6.2 million (~$42,500 USD) for full-time employees
- ¥1.2–1.5 million (~$8,200–$10,300 USD) for part-time workers
Average Salaries by Industry
In this table we outlines the average annual salaries by industry in Japan for 2025. Figures are compiled from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) Monthly Labour Survey, the Statistics Bureau of Japan, and private recruitment platform data such as Mynavi and Daijob.
| Industry | Average Annual Salary (JPY) | Average Annual Salary (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| IT & Software Development | ¥6.8 million | ~$46,600 |
| Finance & Banking | ¥7.5 million | ~$51,400 |
| Engineering & Manufacturing | ¥6.0 million | ~$41,100 |
| Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | ¥5.5 million | ~$37,600 |
| Education (Private Sector) | ¥4.2 million | ~$28,700 |
| Hospitality & Tourism | ¥3.5 million | ~$23,900 |
| Retail & Sales | ¥3.8 million | ~$25,900 |
Where this data comes from:
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) – Monthly Labour Survey 2025
- Statistics Bureau of Japan – Labour Force Survey
- Japan Institute for Labour Policy and Training (JILPT) – Wage structure research
- Japan External Trade Organization (JETRO) – Industry salary insights for foreign professionals
- Mynavi & Daijob – Private recruitment platform salary surveys
Highest-Paying Industries
In 2025, Finance & Banking and IT & Software Development remain at the top of Japan’s salary rankings. These sectors are experiencing strong growth due to digital transformation, global investment trends, and the increasing reliance on advanced technologies.

Finance & Banking: Professionals in investment banking, corporate finance, risk management, and asset management earn some of the highest wages in Japan. Roles in multinational banks and large securities firms in Tokyo often start at ¥8–9 million annually, with senior positions exceeding ¥12–15 million. The rapid rise of fintech companies and digital payment platforms has also created new high-paying opportunities for tech-savvy finance specialists.
IT & Software Development: Japan’s technology sector is undergoing one of its fastest growth periods in decades, driven by major investments in artificial intelligence (AI), cloud infrastructure, 5G deployment, and cybersecurity. The adoption of AI-powered automation in industries such as manufacturing, finance, and logistics is creating a surge in demand for skilled engineers.
Several companies have contributed to this rapid salary increase by competing for top talent:
- Rakuten – Expanding its fintech and e-commerce technology platforms.
- SoftBank – Investing heavily in AI research, 5G networks, and tech startups through the Vision Fund.
- NTT Data – Growing demand for enterprise cloud and digital transformation projects.
- Fujitsu – Shifting to AI-driven and hybrid cloud service models.
- Line Yahoo Japan (LY Corporation) – Innovating in digital payments, AI chat systems, and e-commerce integration.
- Global tech giants in Japan – Amazon, Google, and Microsoft are expanding engineering teams in Tokyo and Osaka.
Key technologies fueling this salary growth include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Machine Learning (ML) – Used in robotics, predictive analytics, and automation.
- Cloud Computing – Rapid adoption of AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud across Japanese enterprises.
- Cybersecurity – Growing demand for specialists to protect against ransomware and data breaches.
- Blockchain – Increasing use in fintech, NFT marketplaces, and supply chain tracking.
- IoT (Internet of Things) – Expanding in smart factories, automotive, and home automation.
- A senior bank executive earning ¥2,000,000/month
- A specialist surgeon earning ¥1,800,000/month
- A senior AI developer at a multinational tech firm earning ¥1,500,000/month
- Labor shortages in critical sectors like IT, healthcare, and advanced manufacturing
- High demand for AI, digital transformation, and new infrastructure projects
- Government incentives encouraging companies to raise wages in response to inflation
- Tokyo & Kanagawa: 15–20% above national average
- Osaka & Nagoya: 5–10% above national average
- Rural prefectures: Often 10–20% lower than national average
- Research industry salary benchmarks Use resources like Robert Half Japan Salary Guide and Michael Page Salary Guide to understand competitive pay ranges for your role and experience level.
- Leverage your Japanese language skills Employers value candidates with JLPT N2 or N1 certification, as it allows you to communicate effectively in the workplace and work with Japanese clients.
- Highlight your unique strengths International work experience, specialized technical skills (e.g., cloud computing, AI, cybersecurity), and professional certifications (e.g., AWS, PMP) can justify a higher offer.
- Negotiate total compensation, not just base salary Benefits such as relocation assistance, housing allowance, transportation subsidies, and paid language training can add substantial value to your package.
- Be culturally sensitive but assertive In Japan, direct confrontation is rare—use polite but confident language, and express enthusiasm for the role while discussing your salary expectations.
As a result, experienced software engineers, cloud architects, and cybersecurity experts can now command salaries well above ¥7–10 million per year, with top specialists in AI and advanced development exceeding ¥12 million annually. This competitive environment is expected to continue driving salaries upward through 2026.
In both industries, bilingual professionals with business-level Japanese (JLPT N2/N1) and international experience have a significant advantage when negotiating salaries. These roles often come with additional benefits such as performance bonuses, stock options, and relocation allowances for overseas hires.
The Evolution of Earnings in Japan: Increases, Incentives, and Next Steps
If you’ve been watching Japan’s wage numbers lately, June 2025 was a real eyebrow-raiser. The average monthly wage jumped to ¥619,893 from ¥337,884 in May, according to the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (via TradingEconomics.com) . On paper, that’s almost a doubling in a month — so what’s going on? The answer is surprisingly simple: June is one of Japan’s bonus months.
Many companies still follow the tradition of paying large lump-sum bonuses in June and December, often worth 2–4 months of salary. These seasonal payouts temporarily inflate the national average, even though most people’s base monthly pay stays exactly the same. It’s a quirk in the data that you need to understand if you’re comparing month-to-month figures.
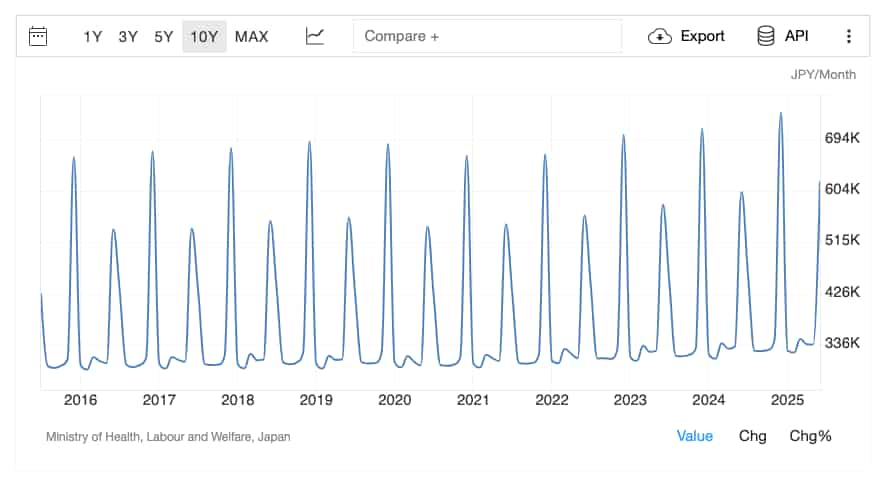
Source: TradingEconomics.com / Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare
Real-life example: An IT engineer earning ¥400,000 per month might get a summer bonus of ¥1,200,000 in June. That month, their total pay jumps to ¥1,600,000 — which skews the “average” upwards, even though their base salary hasn’t changed.
Another reason the national average looks high in certain months is the presence of top earners in the calculation. Senior executives, specialist doctors, and elite engineers can make over ¥1.5–2 million per month. For example:
These outliers raise the average, even though many junior or entry-level professionals earn far less. For context, a PHP developer with about a year of experience might take home ¥220,000–¥280,000/month without bonuses — nowhere near the June “average” wage.
If we zoom out and look at the past decade, wages in Japan follow a familiar pattern: seasonal spikes thanks to bonuses, but a gradual upward climb overall. The main drivers behind this growth include:
That said, the reality on the ground is that salaries often rise more slowly than the cost of living, especially in cities like Tokyo and Osaka. This means your ability to negotiate whether for a new job or during a performance review can make a huge difference to your long-term earnings in Japan.
Regional Salary Differences
Salaries vary significantly by location:

How to Negotiate a Higher Salary in Japan (For Foreign Professionals)
Negotiating a salary in Japan requires preparation, cultural awareness, and confidence. While many job seekers—especially foreigners—accept the first offer, doing so can cost them significant income over time. Here are proven strategies to improve your chances of securing a better salary:
By combining solid research, clear communication, and cultural understanding, you can significantly improve your salary offer in Japan.
Conclusion
Understanding average salaries in Japan by industry gives you a realistic expectation when job hunting or negotiating offers. While some industries like IT and finance lead in pay, location, skills, and experience all influence final salaries. Staying informed ensures you can make the best career decisions in Japan’s evolving job market.
